30 Years of SEO: The History of Search Engine Optimization
SEO has been there long before people started using the Internet for their daily needs, like socializing, shopping, and more. But it’s fair to say that search engine optimization was invented keeping in mind the future of the Internet and how it will be used in the future.
Now, SEO is used everywhere on the Internet. It increases the number and quality of visitors to your site. Hence, you get visitors interested in the products and services you offer.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) has been a cornerstone of digital marketing for over three decades, changing how businesses and users interact on the web .
We have discussed search engine optimization in detail, in this article.
What is Search Engine Optimization?
- SEO is the art and science of optimizing websites to rank higher in search engine results.
- Its importance lies in connecting users with the most relevant content while helping businesses enhance their online presence, drive traffic, and achieve their goals.
- SEO means making your website appear more often on a search engine results page (SERP) and improving its visibility in order to drive organic traffic.
- Its evolution mirrors the changes taking place across the internet landscape driven by technological and user behavioural advancements on the one hand and the relentless pursuit for the most accurate and relevant search results on the other.
This image explains why SEO is so important; it generally drives the majority of traffic on any site. Organic search enhances user engagement on your website.
Do you want your website optimized to make your business successful? Let OPositive optimize your online presence with data-driven SEO techniques that attract, engage, and convert your target audience. With Opositive, your website does not just rank better-it resonates better, ensuring long-term visibility and success.
Why Did Search Engine Optimization Start?
- SEO emerged as a necessity to help businesses stand out online as the Internet grew.
- It aimed to improve website visibility and connect users with relevant content quickly.
- SEO’s evolution is deeply connected to Google, co-founded by Larry Page, whose PageRank algorithm revolutionized search by prioritizing the relevance and quality of web content.
- SEO was initially unregulated. Marketers were engaging in keyword stuffing and link spamming to manipulate the ranking.
- Google took steps to curb these problems by introducing algorithm updates that favoured white-hat SEO practices. Then came ethical optimization, meaningful content creation, and user satisfaction.
- Over time, hundreds of algorithm updates defined the progress of SEO, challenging marketers to be innovative and user-centric.
Opositive’s Approach:
- Establishes E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) to position your business as an industry authority.
- Develops high-quality content and fosters industry engagement to build credibility.
- Increases non-branded traffic by optimizing traffic mix through diversified traffic sources and related topics.
SEO Origin
Origin of SEO dates back to the mid-1990s, coinciding with the rise of the first search engines. SEO began with website owners optimizing their content to rank higher on early search engines like Yahoo and Google. Early SEO involved submitting websites to directories like Yahoo, where ranking depended on relevance and category placement rather than algorithms.
Yahoo was the first human-curated directory where efforts focused on making something visible through proper categorization. Bing, now the second favourite search engine after Google, began in 2009 when MSN Search and Live Search were merged into the current version, the innovation being semantic search and results integration (images, videos, etc.). More insistence by Bing on content quality and clear keyword use ensured more emphasis on click-through rates that extended SEO to more than just Google.
In its infancy, SEO helped websites move from page 4 to page 1 by aligning content with search engine relevance criteria, primarily through keyword optimization and proper submissions.
The history of SEO highlights its role in adapting to evolving search engines like Yahoo, Google, and Bing. Ethical practices and producing valuable, high-quality content remain central to SEO’s effectiveness.
The future of SEO is built on a user-centric approach and meaningful engagement.
Founders of Search Engines and Their Initial Purpose for Users
- 1994: Yahoo was created as an interesting sites directory by Jerry Wang and David Filo, Stanford students. Webmasters manually submitted pages for indexing; AltaVista, Excite, and Lycos also launched.
- 1996: Stanford students Page and Brin developed Backrub, a search engine that ranked sites based on inbound links. Backrub became Google. HotBot, powered by Inktomi, also launched.
- 1997: Danny Sullivan started Search Engine Watch, a website providing search industry news, tips, and ranking advice.
Pioneer SEO Tools in the Early Days of Yahoo and Search Engines
- Yahoo Directory: One of the first human-curated listings for visibility of a website.
- DMOZ (Open Directory Project): One of the major directories that provided free listings and impacted early SEO.
- Overture: Introduced PPC advertising and changed keyword strategies.
- AltaVista: Introduced full-text indexing, which boosted content optimization.
- Excite: Kept the focus on keyword relevance and search behaviour.
- WebCrawler: First, index whole web pages, encouraging content-rich SEO.
- Inktomi: Powered Yahoo and others, emphasizing keywords and meta tags.
- Alexa Toolbar: Provided website rankings and traffic analytics.
- Hitbox/WebTrends: Used to track user behaviour for better SEO strategies.
Early Days of Search Engines (Pre-1990s)
Before modern search engine directories like Yahoo and primitive tools like Archie (1990) helped users find information, websites were indexed manually, making visibility a challenge. This era marked the beginning of web cataloguing but lacked any formal optimization techniques.
The Birth of SEO in the Mid-1990s
The term “SEO” emerged alongside the rise of early search engines such as AltaVista, WebCrawler, and Lycos. As businesses realized the value of being found online, organizations started using early optimization techniques such as keyword placement and meta tags to gain better positions. Knowing the brief history of SEO helps marketers understand what works and what does not and adapt to future advancements effectively.
Timeline of Evolution of SEO:
To understand the evolution of SEO, we have prepared an SEO history timeline and divided the whole journey into three parts.
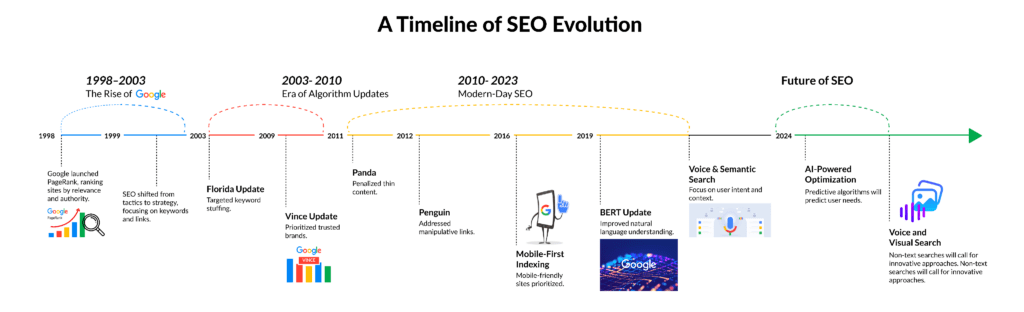
Rise of Google (1998-2003)
Google came up with its PageRank algorithm in 1998, which ranked websites on the basis of relevance and authority. It puts keyword-based SEO into great importance because websites must be optimized to meet Google standards, marking the beginning of strategic optimization.
The Era of Algorithm Updates (2003–2010)
The mid-2000s saw the introduction of major algorithm updates.
- Panda: It was a filter meant to punish thin and bad content. Due to this update, one must continuously reevaluate and upgrade the website’s content.
- Penguin: Targeted toward manipulative link-building practices. The update was made to battle the web spam. Under this update, every website was found to use black hat SEO strategies to influence the results, and these sites got punished.
- The Google Florida Update of 2003 was a major algorithm update aimed at fighting keyword stuffing and improving the relevance of search results, marking a turning point toward user-centric SEO practices.
- The Google Vince Update of 2009 addressed the ‘cesspool’ issue in search results by favouring trusted, authoritative brands, which enhanced the quality and reliability of search rankings.
These updates transformed SEO from keyword stuffing to producing relevant, high-quality content.
Modern-Day SEO (2010–2023)
In recent years, SEO has evolved into a sophisticated practice.
- Mobile First Indexing
– Websites developed for mobile devices receive higher rankings.
- Voice Search
– Answers in the form of regular conversational content are required by queries using virtual assistants.
- AI and Semantic Search
– Google is keen on its BERT and RankBrain models that focus more on the intent of a query.
Machine learning revolutionizes search through the ability of algorithms to better understand user intent, personalize results, and adapt to changing behaviours, thereby making searches faster and more relevant.
Google AdSense, Google My Business, and YouTube also play very important roles in SEO by monetizing content, enhancing local search visibility, and driving traffic through video optimization and engagement.
Today, social profile signals like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn engagements indirectly impact SEO rankings through increased content visibility, traffic, and brand authority.
How Have SEO Trends Changed Over Time?
SEO has changed the marketing game from keyword-based to a more holistic approach, incorporating content quality and technological integration with user experience.
Crawling, Indexing, and Ranking Evolution
In the past 10 years, crawling, indexing, and ranking have evolved from basic keyword matching to sophisticated AI-driven algorithms that prioritize user intent, content quality, mobile-first indexing, and real-time updates, fundamentally reshaping the SEO landscape.
- Crawling
Search engines use web crawlers to find new pages and track the latest information. These are little spiders that crawl all over the Internet and gather information. Crawlers follow links from already known pages to new ones that have not yet been found. The whole process of discovering new information is called crawling.
- Indexing
After the crawling process, now that the search engine has updated information, it’s time to organize it, and is referred to as indexing. Data can be accessed after a search if it’s performed after getting processed and saved in the index. Indexing is essential for every website because it supports being found on the Internet.
- Ranking
It is the final step in the search process. Search engines determine where different pieces of content or URLs should appear in search engine results pages using their algorithm. This whole process is called ranking.
The Influence of User Behavior and Technology
Advances in technology, such as mobile devices, AI, and augmented reality, along with user behaviour shifts toward instant gratification and personalized experiences, have consistently reshaped SEO strategies.
What is Search Engine Marketing?
- Search Engine Marketing (SEM) is a digital marketing strategy focused on increasing a website’s visibility on search engine results pages (SERPs) through paid advertising.
- It involves strategies like Pay-Per-Click (PPC) advertising, where advertisers pay each time their ad is clicked.
- Keyword targeting is essential in SEM, where ads are shown based on user searches for specific keywords.
- SEM includes paid search ads on platforms like Google Ads, Bing Ads, and Yahoo Ads.
- Paid search campaigns can be highly targeted by location, time, device, and other factors.
- SEM is often used alongside SEO to achieve both organic and paid visibility in search results.
- ROI-focused: SEM allows for measurable results and budget control based on performance.
Role of Search Engine Marketing in History of SEO
Search Engine Marketing (SEM) complements SEO by integrating paid strategies such as Pay-Per-Click (PPC) campaigns to increase visibility. While SEO focuses on organic rankings, SEM uses advertising to secure top positions on SERPs, enhancing the overall effectiveness of online marketing.
SEM began alongside SEO, integrating paid advertising with organic optimization to secure better rankings and visibility. The history of search engine marketing reveals how businesses have evolved from simple keyword targeting to complex, data-driven strategies to reach their audience effectively.
Impact of Google Algorithm Updates on SEO
Every Google update refined the search experience:
- Hummingbird: semantic search for deeper insight into user queries. The upgrade underlined Google’s commitment to a better understanding of what the searcher is asking. The update leverages context and query intent so that results can fit the consumer’s needs, and so do local searches become more specific.
- Mobilegeddon – Google took up this algorithm update to enhance its user experience since mobile devices represent more than half of all Google searches. The impact was enormous for mobile searches and touched all mobile searches in all languages around the world.
- Pigeon- This was to integrate Google’s local algorithms more deeply into their traditional web algorithm. This means, as a consequence of this, there is an even greater motivation for local businesses to vie for the ranking in terms of having a strong web presence.
- E-E-A-T, or Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness has raised the quality bar on content.
- Exact Domain Match – This update was done in such a manner that sites that have low domain and page authority don’t rank high due to relevant domain names.
- Fred – This update was the removal of low-quality results. Because of this update, many affiliate sites got hurt. After the implementation of this update, the sites started working to deliver quality material to attract high-quality links.
- Intrusive Interstitials Update – This update was released by Google to make surfing on mobile devices easier. In this update, interstitials appear on pages as the user scrolls through the content.
- Medic – The medic update mainly targeted health and financial websites. Google mentioned that there was no “cure” for pages that might have been affected except to keep creating excellent content.
- BERT- Commonly known as Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers. This update improved the way Google processes a search query. Also, because of this update, on-page components become critical in terms of precisely employing words. For instance, the BERT algorithm impacts how it can understand the context of search queries such as interpreting ‘2019 Brazil traveller to USA need a visa,’ wherein it identifies the intent to be about a Brazilian traveller requiring a visa for a trip to the USA thereby improving accuracy in results.
These changes made marketers adjust their focus from technical manipulations to user-centric strategies.
A Glimpse into the Future of SEO
Internet has undergone a revolution of unparalleled dimensions. So, have user behaviour and mannerisms. Innovations from voice search to AI to machine learning and enhanced algorithms transformed the face of search optimization.
While one can hardly predict the exact future of SEO, something is quite certain – it’s upwardly mobile. Moving ahead, the focus would largely be on delivering more personal and refined user experience; the focus would be on intent-driven and high-quality original content.
This development is needed because users need search results that provide quick, context-rich insights with minimal effort. The trend towards constant connectivity and predictive content solutions is further highlighted by the emergence of smart devices and wearables. SEO will continue to evolve to meet these expectations and will remain at the forefront of the digital experience.
The future of SEO will include more personalization and technology integration.
- AI-Powered Optimization: Predictive algorithms will predict user needs.
- Voice and Visual Search: Non-text searches will call for innovative approaches.
- Sustainability in Digital Marketing: Green practices and ethical content creation will be the highlight.
Conclusion
We know that search engine optimization is used to display a website’s rating on Google, and it has been changing and evolving since its inception. Here in this article, we have covered how it has changed over the years.
So, if you want to take your website to the top, you better keep tabs on Google algorithm updates and their impact on SEO practices. So keep experimenting with different content, but make sure to use only white hat practices.
The history of Search Engine Optimization reflects the Internet’s growth from static pages to a dynamic, user-focused ecosystem. As SEO continues to evolve, its fundamental goal remains the same: connecting users with the most relevant and valuable information. Staying ahead in the evolution of SEO requires adapting to technological advancements and understanding user intent, ensuring a sustainable and impactful online presence.
Opositive is a company that elevates a website’s organic search presence by optimizing on-page and off-page elements. Opositive also amplifies incoming traffic using advanced SEO techniques like long-tail keyword optimization and content marketing. Opositive combines creativity and analytics to design SEO campaigns that keep you ahead in the evolving digital landscape. So, elevate your online game with OPositive’s SEO expertise – where strategy meets measurable results.
Like what you read? Share with a friend or colleague.