How Search Engines Work: Crawling, Indexing & Ranking Explained
When someone types a query into Google and gets thousands of results in under a second, it feels effortless. But if you are responsible for growth, traffic, or leads, you cannot treat that as magic. You need a clear, no-nonsense understanding of how search engines work so that every page you ship actually has a chance to be found.
Under the hood, all modern search engines follow the same core pattern:
- They discover pages.
- They understand and store information about those pages.
- They decide which pages should appear for each search.
This guide walks through those steps in depth – crawling, indexing, and ranking with a focus on how Google works in real-world conditions, not just theory.
How Search Engines Work: Understanding Search Engine Basics
Let us start simple. A search engine is basically a very fast, very picky librarian for the internet.
Instead of walking into a physical library to ask for a book, users type their search terms into a search bar. The search engine’s job is to:
- Scan through a huge internal library of pages.
- Work out which ones are relevant and trustworthy for the query.
- Show the best possible answers in a format that is easy to click and consume.
Why do search engines exist at all?
Because the web is messy. New pages go live every second. Old content is deleted, moved, or updated. Without a system that constantly organises this chaos, users would never find what they need.
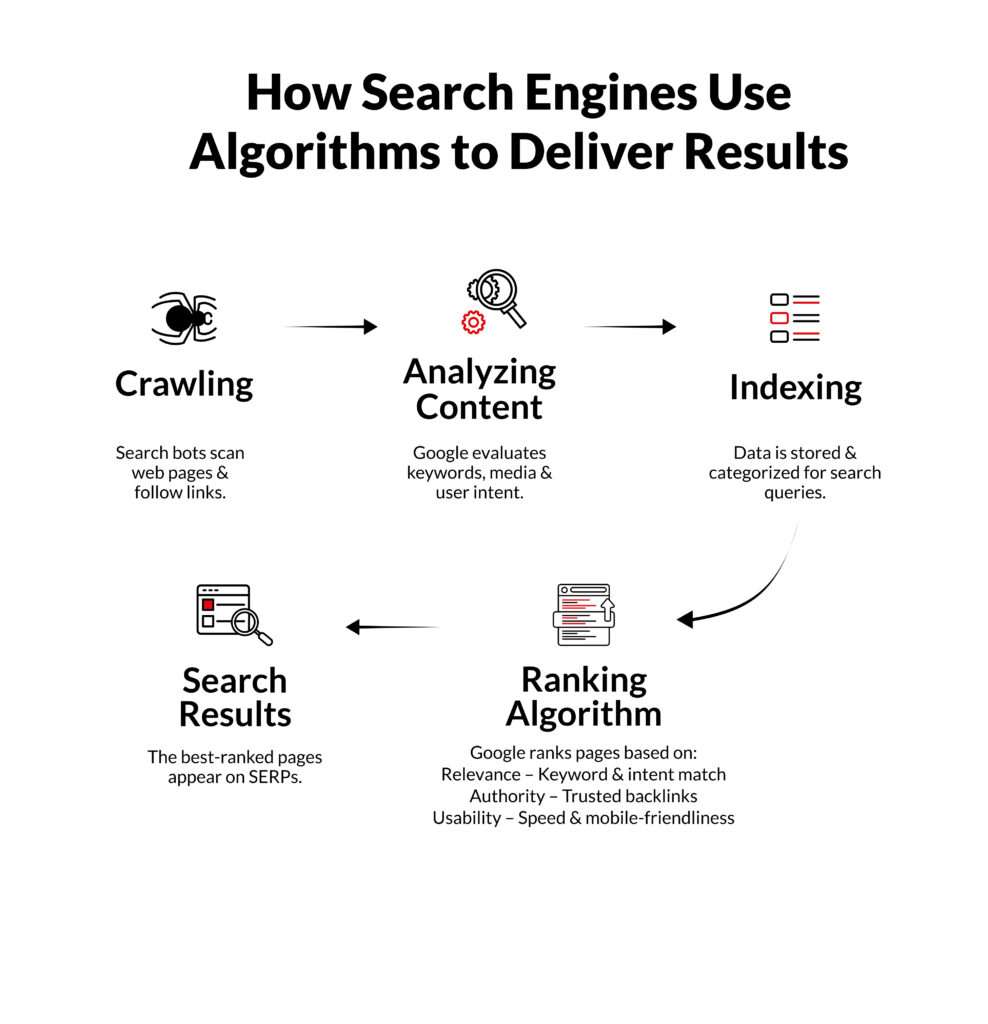
In practice, how a search engine works boils down to three core mechanisms:
- Crawling – sending automated bots (crawlers/spiders) to find URLs.
- Indexing – processing the content and storing structured information in a gigantic database.
- Ranking and serving – choosing which pages to show (and in what order) when a search happens.
Everything you do in SEO eventually touches one of these three stages.
Search Engine Basics: The Three Stages of How Search Engines Work
Search engines may look different on the surface, but most follow the same basic workflow:
- Crawl
- Render (where needed)
- Index
- Rank
- Serve
Each step builds on the previous one. If crawling is blocked, nothing gets rendered or indexed. If indexing fails, ranking is impossible. That’s why search engine basics are so important for anyone investing in content or growth.
How the Google Search Engine Works
In everyday conversations, when someone asks how search engines work, they usually mean Google.
At a high level, this is how Google operates:
Crawling
Googlebot discovers URLs using sitemaps, internal links, external links, RSS feeds, and other hints. It respects robots.txt and crawl rules, and it schedules visits based on your site’s perceived importance and health.
Indexing
Once a page is fetched, Google tries to understand it. It looks at your content, headings, links, meta tags, images, structured data, and many other signals. Then it decides whether this URL is worth storing in its index and how it relates to different pages.
Serving & ranking
When a user searches, Google does not go back to the live web. It searches its own index and runs ranking algorithms to decide which pages are the best match for that query at that moment.
If you want your on page seo work to pay off, your pages need to pass smoothly through all three of these phases.
How the Google Search Engine Works Step by Step
If we zoom in further, this is how Google search engine works step by step for a new or updated page:
1. Discovery
A new URL appears in a sitemap, is linked from another page, or is submitted via Search Console.
2. Crawling
Googlebot requests the URL and downloads the HTML and other resources that are allowed. If robots.txt or meta robots say “do not crawl”, this is where the journey ends.
3. Rendering
For pages that rely heavily on JavaScript, Google may render them to see the final version users get in their browsers. This is especially important for content injected after load.
4. Indexing
The content is extracted and analysed. Google decides what the page is about, how it connects to other URLs, and whether it should be stored in the index.
5. Ranking
When someone searches, the page is evaluated against hundreds of signals: relevance to the query, content quality, freshness, links, user experience, and more.
6. Serving
If your page wins enough of these mini-competitions, it is shown on the SERP for relevant searches.
Think of it as a pipeline: crawl → render → index → rank → serve. If you understand this, a lot of SEO confusion suddenly disappears.
How Search Engines Rank Pages: The Algorithm Behind Search Results
Once a page makes it into the index, the next step is competition: how search engines rank pages against each other for a specific query.
The exact formulas are secret, but the main ideas are well known and stable over time.
Key ranking signals
Here are the broad categories that matter most:
- Content quality and relevance
Does your page genuinely answer the searcher’s question? Is it original, complete enough, and written in a way that people can actually use?
- Authority and backlinks
Links from other sites act a bit like recommendations. A relevant link from a strong, trustworthy site is worth far more than dozens of weak, random links.
- User experience
Is the site fast, mobile-friendly, and easy to navigate? Are there annoying pop-ups or layout shifts? Google increasingly cares about how smooth the experience is.
- Technical health
Clean URLs, correct HTTP responses, secure connections (HTTPS), and stable infrastructure all help search engines trust your site.
How search intent affects rankings
Search engines do not just match keywords; they try to match intent.
- Someone searching “how search engines work” is clearly looking for an explainer, not a product page.
- Someone searching “best enterprise SEO tool” is evaluating options and expects comparisons, pricing, and proof.
If your content format and angle don’t match intent, no amount of links or optimisation will fully fix it. This is where off page seo and content strategy need to align: authority gives you a chance to rank, but intent match keeps you there.
Why is ranking different from indexing
A common mistake is assuming “indexed = doing well”. That is not true.
- Indexing means Google knows your page exists and has stored it.
- Ranking means your page beats many others for a specific query and earns a visible position.
You can be indexed and still be buried on page 7 because your content is too thin, the topic is unclear, your competitors are better, or your site does not have enough authority yet.
How Does Search Engine Indexing Work
To understand why some URLs never show up anywhere, you need a clearer view of how search engine indexing works.
Indexing is basically the organisation step. When Google indexes a page, it:
- Read the main content and headings.
- Look at internal and external links pointing in and out.
- Take note of meta tags, canonical tags, and robots instructions.
- Checks images, alt text, and sometimes other media.
- Reads structured data to identify entities like products, FAQs, or organisations.
Not every page that gets crawled is indexed. Common reasons a URL might be skipped or dropped include:
- It is blocked with noindex or disallowed in robots.
- The content is extremely thin or a near-duplicate of another URL.
- The page looks low quality or spammy.
- Google has a better version of the same content on a different URL.
This is where technical seo and content decisions blend. Clean information architecture, clear canonical tags, and a focus on useful pages greatly increase your chances of being properly indexed.
Search Engine Basics for Crawling, Indexing & Ranking in Real-World Scenarios
Theory is nice, but teams run into problems when they try to apply search engine basics on actual websites with legacy code, multiple teams, and business pressure.
How search engines understand web pages
Search engines do not “see” your design the way users do. They mainly work with:
- Text content and headings.
- Link structures (internal and external).
- Metadata like titles, descriptions, and robots directives.
- Structured data that labels key pieces of information.
- File-level details like status codes and canonical signals.
This is why SEO cannot be something you bolt on at the end. Product, development, content, and design all leave fingerprints that affect how bots understand your site.
Text, metadata, multimedia & structured data
To make your pages easier to interpret:
- Use clear, descriptive headings and subheadings.
- Keep title tags focused and honest about what’s on the page.
- Write alt text that actually describes images.
- Use schema markup where it makes sense (FAQs, products, articles, reviews, etc.).
You are not doing this for decoration. You are giving search engines a clean, structured version of reality so they can confidently surface your content.
Handling JavaScript, duplicate content & canonical tags
Modern stacks introduce extra complexity:
- JavaScript: If crucial content appears only after heavy scripts run, check how it looks to a non-JS user agent. In many cases, server-side rendering or hydration tweaks make a big difference.
- Duplicate content: E-commerce, faceted navigation, UTM parameters, and print versions can easily create multiple URLs with very similar content.
- Canonical tags: Canonicals tell search engines which version of a set of similar URLs is the “main” one. Use them carefully, test them, and avoid conflicting signals.
This is exactly the type of thing a regular seo audit should catch before it quietly harms performance over months or years.
How Search Engines Work on the SERP: Delivering the Final Results
All of this background work pays off when a user finally sees something on the search results page.
How search engines pull ranked results for users
The moment someone hits “search”, a lot happens behind the scenes:
- The query is analysed: language, intent, possible spelling corrections, location signals, and device type.
- A pool of relevant documents is pulled from the index.
- Ranking systems score and sort those documents.
- The final layout of the SERP is decided – which features to show, how many organic results, whether to show images, maps, or videos.
From the user’s perspective, it is just a list of answers. From your perspective as a marketer or growth leader, it is the final reflection of how well you have aligned with how search engine work across all stages.
Types of SERP features: blue links, snippets, rich results
Traditional organic results (“blue links”) still matter, but they are only part of the story. Depending on the query, you may also see:
- Featured snippets.
- “People Also Ask” boxes.
- Image or video carousels.
- Local packs and maps.
- Knowledge panels for entities and brands.
Your content strategy should account for this. For some queries, aiming for a featured snippet (with tight Q&A formatting) makes sense. For others, local visibility or rich product results will matter more.
Why do some pages appear more prominently
The pages that consistently show up in prime real estate tend to:
- Match intent clearly.
- Have strong topical depth and authority.
- Load quickly and work well on mobile.
- Earn trust through links, mentions, and brand recognition.
At that stage, you are competing not just on keywords but on expertise. This is where partnering with experienced SEO Experts can help you avoid trial-and-error and move straight to strategies that align with where Google is heading.
Common Issues That Disrupt How Search Engine Works
In real projects, the problems that hurt performance are often invisible at first glance. A site can look fine to users and still be difficult for crawlers.
Crawl budget limitations
For small sites, crawl budget is rarely a major issue. For large sites, it can be painful.
Examples:
- Every filter combination generates a unique URL.
- Old tag pages or thin archives are still live.
- Infinite scroll or calendars create hundreds of almost-empty pages.
If Googlebot spends a lot of energy on junk or low-priority URLs, important pages may be crawled less often. Over time, that means slower updates in the index and weaker visibility.
Indexing failures
Even when crawling happens, indexing can fail or be partial. Typical reasons include:
- Soft 404s where pages technically load but have little real content.
- Conflicting signals from canonicals, redirects, and meta robots.
Content that looks generic or spun compared to the index. - Server errors or timeouts that make the site look unreliable.
When you know how a search engine works at the indexing layer, a lot of these issues become easier to diagnose and fix.
Ranking drops from quality or technical issues
Sudden ranking drops are rarely random. They often line up with:
- Quality updates where search engines tighten standards.
- Large redesigns or migrations done without mapping URLs and redirects correctly.
- A series of technical problems (downtime, security issues, spam injections).
Regular health checks, meaningful on page seo improvements, and a solid monitoring setup make these less scary. You will still see fluctuations, but you will know where to look and what to test.
Why Understanding How Search Engine Works Matters for SEO
It is tempting to treat SEO as a list of tricks or quick wins. In practice, brands that win long-term understand the engine itself.
Strategic importance of crawlability & indexability
If bots cannot reach or understand your key pages, nothing else matters. It is like printing brochures and keeping them in a locked storeroom.
Good basics include:
- Clear navigation and internal linking.
- Logical URL structures.
- Helpful sitemaps and clean robots rules.
- Fast, stable responses from your servers.
Get these rights and every new initiative lands on a stronger foundation.
Why ranking depends on technical + content alignment
You cannot separate “content” and “tech” into two disconnected lanes anymore.
- Strong content on a broken platform underperforms.
- Perfect technical hygiene without meaningful content also underperforms.
Real results come when technical seo, product decisions, content strategy, and even brand work in the same direction. That’s also the point at which competitors find it hard to copy you quickly.
How brands benefit from mastering search engine basics
Once teams grasp search engine basics, conversations change:
- Stakeholders understand why some ideas are low-leverage.
- New sections or product launches are planned with search in mind from day one.
- You can forecast better, not just react.
For an agency or in-house team, this clarity turns SEO from a “black box” into a predictable growth lever.
Conclusion: How Search Engines Work & Why Optimizing for Each Stage Matters
To pull it all together:
- Crawling is how search engines discover your pages.
- Indexing is how they process and store information about those pages.
- Ranking and serving determine what to show and in which format when someone searches.
If you optimize only one part of this chain, you get partial results. To build real visibility, you need to:
- Make discovery easy.
- Make understanding straightforward.
- Make your content the best possible match for the queries that matter.
An experienced partner like Opositive can help you build that system end to end – from technical clean-up and content planning to link strategy and measurement – so that every campaign sits on a solid search foundation and keeps compounding over time.
Whether you are reviewing templates, planning new content, or considering a full site overhaul, start by revisiting how search engines work. The more closely you align with that mental model, the less you will rely on guesswork and the more predictable your organic growth becomes.
FAQs
What is a search algorithm?
A search algorithm is the “rulebook” a search engine uses to decide which pages should appear for a query and in what order. It weighs many factors – relevance, content quality, freshness, links, user behaviour, and more – to estimate which results will be most useful for the searcher.
What is a crawler or spider in a search engine?
A crawler (also called a spider or bot) is an automated program that travels across the web by following links and sitemaps. Its job is to discover new pages, revisit old ones, and return that data so the search engine can index and rank them.
What is the difference between crawling and rendering?
- Crawling is when the bot requests a URL and fetches the raw HTML and related resources.
- Rendering is when the search engine processes HTML (and any JavaScript) to see the final version of the page as a user’s browser would.
On simple, static pages, these are almost the same. On JavaScript-heavy sites, rendering is a separate, important step.
What is a crawl budget, and why does it matter?
Crawl budget is the rough limit on how many URLs a search engine will crawl on your site within a certain timeframe. It depends on factors like site size, importance, and server health.
If your site generates endless low-value URLs – for example, filter combinations or thin archives – crawlers may waste time there and visit your important pages less often. For large and complex sites, managing crawl budgets is a key part of advanced SEO planning.